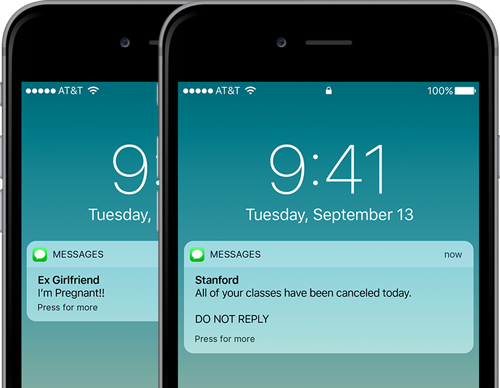
In today’s interconnected world, SMS (Short Message Service) spoofing has emerged as a significant concern for individuals and businesses alike. SMS spoofing refers to the practice of manipulating the sender’s information to make it appear as if a message is coming from someone or somewhere else. While the technology behind SMS spoofing can be complex, its implications are straightforward and potentially harmful.
What is SMS Spoofing?
SMS spoofing involves the falsification of the sender’s information in a text message. Unlike legitimate messages, where the sender’s information accurately reflects the origin of the message, spoofed SMS messages can display any sender’s name or number, regardless of their actual identity.
Risks Associated with SMS Spoofing:
- Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals often use SMS spoofing as a tactic to launch phishing attacks. By impersonating trusted entities such as banks, government agencies, or legitimate businesses, attackers can trick recipients into divulging sensitive information like passwords, credit card numbers, or personal details.
- Identity Theft: SMS spoofing can facilitate identity theft by impersonating individuals or organizations in fraudulent communications. This can lead to financial loss, reputational damage, and legal consequences for both the victim and the impersonated party.
- Malware Distribution: Spoofed SMS messages may contain malicious links or attachments designed to infect recipients’ devices with malware. Once installed, malware can compromise the security and privacy of users’ data, as well as exploit vulnerabilities within their devices or networks.
Prevention Strategies:
- Verify Sender Identity: Always verify the authenticity of SMS messages, especially those requesting sensitive information or urgent action. Contact the purported sender through official channels to confirm the legitimacy of the communication.
- Enable Sender ID Verification: Implement sender ID verification mechanisms to validate the authenticity of incoming SMS messages. By authenticating sender identities, businesses and individuals can mitigate the risk of falling victim to spoofed messages.
- Educate Users: Raise awareness among users about the risks associated with SMS spoofing and provide guidance on identifying suspicious messages. Educating individuals about common phishing tactics and red flags can empower them to exercise caution when interacting with SMS communications.
- Use Trusted Messaging Platforms: Utilize trusted messaging platforms and service providers that employ robust security measures to prevent SMS spoofing and safeguard user communications. Research and select reputable providers that prioritize security and compliance with industry standards.
- Report Suspected Incidents: Promptly report suspected instances of SMS spoofing to relevant authorities, telecommunications regulators, or cybersecurity organizations. Reporting incidents helps to mitigate the impact of spoofing attacks and contributes to collective efforts to combat cyber threats.
In conclusion, SMS spoofing poses significant risks to individuals, businesses, and the integrity of digital communications. By understanding the nature of SMS spoofing, implementing preventive measures, and fostering a culture of vigilance, users can mitigate the threat posed by spoofed messages and protect themselves against cyber attacks. Through collaborative efforts and proactive security measures, we can work towards a safer and more secure digital environment for all.